Verification of Compensation Theorem 
Theory
In a linear time invariant network when the resistance `(R)` of an uncoupled branch, carrying current (I), is changed by ΔRL , the currents in all the branches would change and can be obtained by assuming that an ideal voltage source of Vc has been connected such that Vc=IΔRL in series with R+ΔRL when all other sources in the network are replaced by their internal resistances.
Explanation :
Let us assume a load `R_L` connected to a dc source network whose thevenin's equivalent gives Vo as the Thevenin's voltage and RTh as Thevenin resistance.
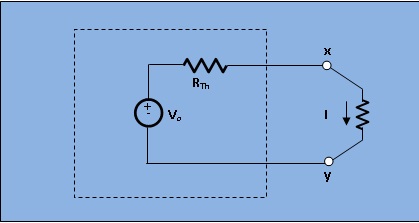
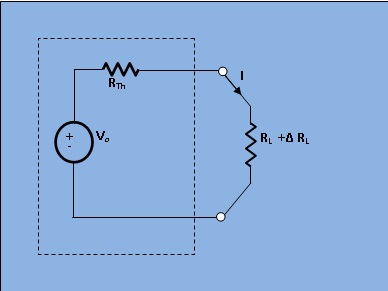

Let the load resistance Rl be changed to R+ΔRL.Since the rest of the circuit remains unchanged,the Thevenin equivalent network remains the same.This Change of current being termed as ΔI , we find
$$\Delta I = I' - I$$
$$= \frac{V_o}{(R_{Th} + R_L + \Delta R_L)} - \frac{V_o}{(R_{Th} + R_L)}$$
$$= \frac{V_o (-\Delta R_L)}{(R_{Th} + R_L)(R_{Th} + R_L + \Delta R_L)}$$
$$= -\frac{V_c}{R_{Th} + R_L + \Delta R_L} .......(3)$$
$$V_c = I \Delta R_L$$
This voltage Vc is termed as compensating voltage.
